Web Browsers
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them correctly.
A browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
HTML Page Structure
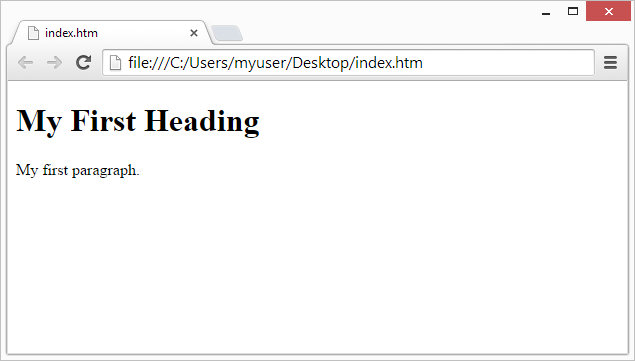
Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:
<html>
<head>
<title>Page title</title>
</head><body></body>
</html><h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>This is another paragraph.</p>
Note: The content inside the <body> section (the white area above) will be displayed in a browser. The content inside the <title> element will be shown in the browser's title bar or in the page's tab.
HTML History
Since the early days of the World Wide Web, there have been many versions of HTML:
| Year | Version |
|---|---|
| 1989 | Tim Berners-Lee invented www |
| 1991 | Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML |
| 1993 | Dave Raggett drafted HTML+ |
| 1995 | HTML Working Group defined HTML 2.0 |
| 1997 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 3.2 |
| 1999 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 4.01 |
| 2000 | W3C Recommendation: XHTML 1.0 |
| 2008 | WHATWG HTML5 First Public Draft |
| 2012 | WHATWG HTML5 Living Standard |
| 2014 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5 |
| 2016 | W3C Candidate Recommendation: HTML 5.1 |
| 2017 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5.1 2nd Edition |
| 2017 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5.2 |
This tutorial follows the latest HTML5 standard.
No comments:
Post a Comment